Gingivoplasty and clinical crown augmentation are dental procedures that aim to improve the aesthetics and health of your gums and teeth.
These procedures can be indicated to correct problems such as excess gum tissue, short teeth or to prepare the area for dental restorations.
Gingivoplasty is a surgical procedure that reshapes the gums to create a more aesthetic and healthy gingival contour.
It is often performed to correct
– Gummy Smile: When there is excess gum visible when smiling.
– Gingival inequality: To even out the level of the gums around the teeth.
– Preparation for Restorations: In cases where a specific gingival contour is required for dental crowns or veneers.
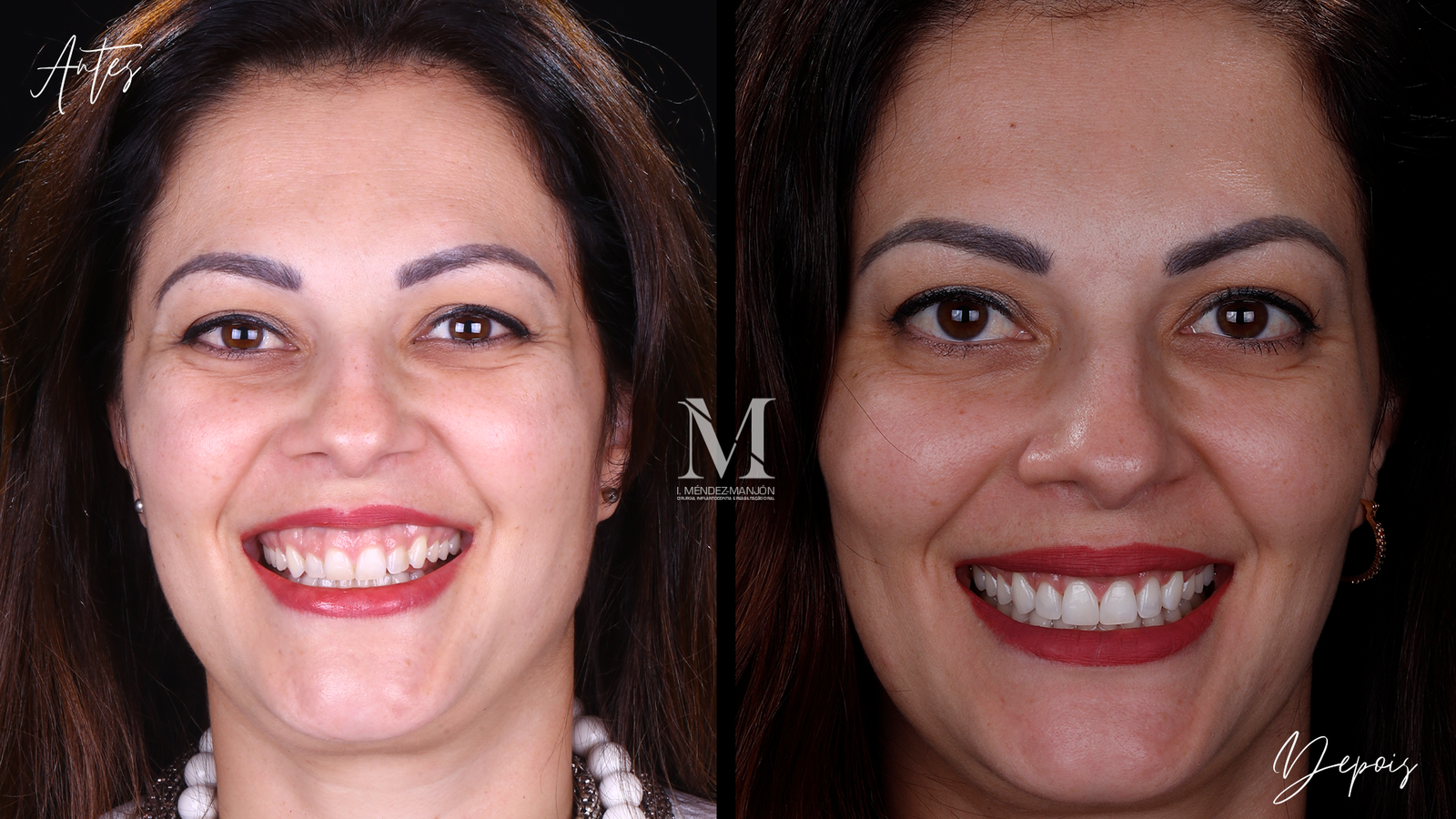

Clinical crown augmentation involves removing gum tissue and/or bone to expose more of the tooth’s surface.
This procedure is indicated for:
– Preparation for Crowns: When more tooth needs to be exposed for the placement of crowns or bridges.
– Subgingival caries: To treat caries or fractures below the gum line.
– Dental Aesthetics: To increase the visible height of the teeth, improving the appearance of the smile.
To ensure a quick and effective recovery, follow these guidelines:
– Oral Hygiene: Keep the operated area clean by following the dentist’s instructions, using a soft-bristled toothbrush and antiseptic mouthwash.
– Medication: Take the prescribed medication to relieve pain and prevent infection.
– Diet: Opt for soft foods and avoid hot or spicy foods. Food: Opt for soft foods and avoid hot or spicy foods for the first few days.
– Activities: Avoid intense physical activity and follow the dentist’s recommendations on rest.
– Follow-up appointments: Attend all follow-up appointments to monitor healing.
Periodontal disease, also known as periodontitis, is an inflammatory condition that affects the gums and the bone that supports the teeth.
If not treated properly, it can lead to tooth loss and other health problems.
The good news is that, with early diagnosis and proper treatment, it is possible to control the disease and maintain optimal oral health.
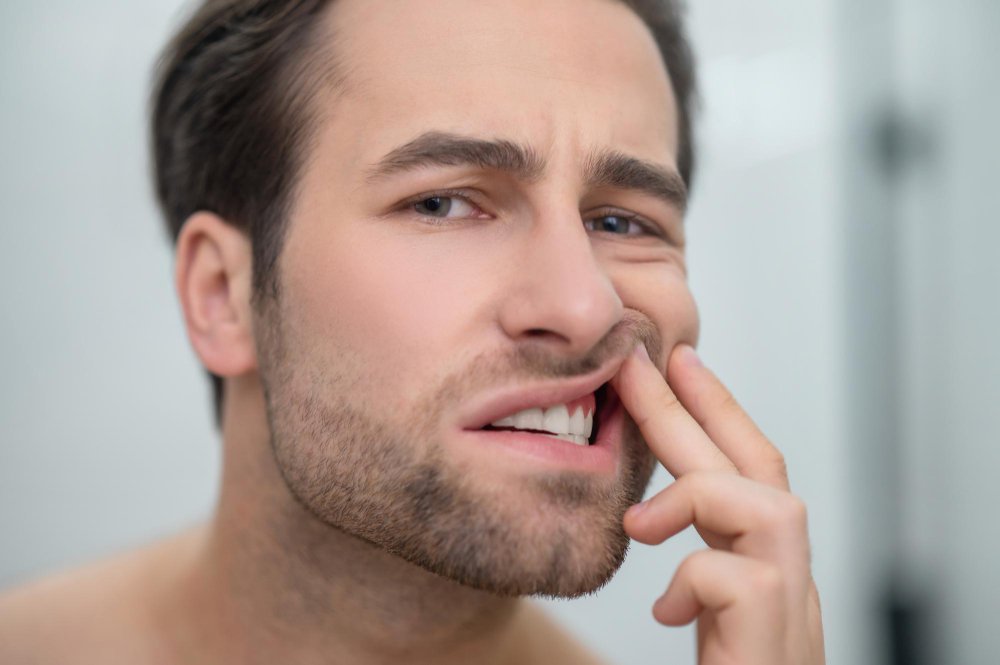

Periodontal disease begins with inflammation of the gums, called gingivitis.
If left untreated, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis, where the inflammation spreads to the bone and supporting tissue of the teeth.
The main symptoms include:
– Red, swollen gums that bleed easily
– Persistent bad breath
– Gum recession
– Pockets forming between the gums and teeth
– Tooth mobility
The main cause of periodontal disease is the build-up of plaque on the teeth and gums.
Other risk factors include:
– Poor oral hygiene
– Smoking
– Diabetes
– Hormonal changes (such as pregnancy)
– Antibiotics: In some cases, topical or systemic antibiotics may be prescribed to control the bacterial infection.
– Periodontal Surgery: In more advanced cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to reduce periodontal pockets and regenerate lost tissue.
Examples include:
– Flap Surgery: The gums are lifted to remove deep tartar and reduce pockets.
– Tissue Grafts: These can be used to regenerate lost bone and gums.
– Bone Surgery: The bone affected by periodontitis is softened to allow the gums to fit better.
To ensure effective treatment and prevent recurrence of periodontal disease, follow these guidelines:
– Oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft toothbrush and floss daily.
– Mouthwash: Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to help control plaque.
– Healthy diet: Avoid foods high in sugar and maintain a balanced diet.
– Avoid smoking: Smoking can worsen periodontal disease and delay healing.
Copyright © Irene Méndez-Manjón | Developed by Libelle Comunicação
Fale Conosco